The Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) standard has revolutionized the way medical images are stored, shared, and viewed across the healthcare industry. With its widespread adoption, a variety of devices and systems have been developed to support DICOM, making it the backbone of medical imaging workflows. This blog post will delve into what DICOM-compatible systems are, which devices support DICOM, their features, and how DICOM data can be viewed, analyzed, and accessed. By the end of this post, you’ll have a clear understanding of the ecosystem that supports DICOM and how it enhances the efficiency and accuracy of medical imaging.
What Are DICOM-Compatible Systems?
DICOM-compatible systems are those that adhere to the DICOM standard, ensuring they can create, store, transmit, and display medical images and related information. These systems include a wide range of devices and software used in medical imaging, such as MRI machines, CT scanners, ultrasound devices, and specialized workstations for viewing and analyzing images.
The compatibility with DICOM ensures that images and data can be shared seamlessly across different devices and systems, regardless of the manufacturer. This interoperability is critical in modern healthcare environments where patient data often needs to be accessed from multiple locations and by various healthcare professionals.
Devices That Support DICOM
-
Imaging Modalities
The most common DICOM-compatible devices are imaging modalities, which are the machines that create medical images. These include:
-
MRI Machines: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machines are one of the primary devices that support DICOM. They produce detailed images of the internal structures of the body, and these images are stored and transmitted using the DICOM standard.
-
CT Scanners: Computed Tomography (CT) scanners generate cross-sectional images of the body using X-rays. Like MRI machines, CT scanners are fully integrated with the DICOM standard, allowing the images to be easily shared and accessed.
-
Ultrasound Devices: Ultrasound machines use sound waves to create images of internal organs and tissues. These devices are DICOM-compatible, enabling the images to be stored in a standardized format for further analysis.
-
X-ray Machines: Traditional X-ray machines, as well as more advanced digital radiography systems, use DICOM to store and transmit the images they produce. This standardization is crucial for maintaining consistent image quality across different systems.
-
Nuclear Medicine Systems: Devices used in nuclear medicine, such as PET and SPECT scanners, also support DICOM. These systems generate images that require careful handling and precise storage, both of which are facilitated by DICOM.
-
-
Workstations and Viewing Systems
In addition to the devices that generate images, there are numerous workstations and software systems designed to view, analyze, and manipulate DICOM images. These include:
-
PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems): PACS are one of the most common types of DICOM-compatible systems. They store and retrieve medical images from various modalities and allow for the viewing and sharing of these images across the healthcare enterprise. PACS also integrate with other healthcare IT systems, such as electronic health records (EHRs), to provide a comprehensive view of patient data.
-
RIS (Radiology Information Systems): RIS is another key component of the medical imaging workflow. It manages radiology-related data and integrates with PACS to provide a seamless workflow from image acquisition to diagnosis. RIS systems are fully DICOM-compatible, ensuring that images and associated data are consistently and accurately stored.
-
DICOM Viewers: DICOM viewers are specialized software applications designed to display DICOM images. These can range from basic viewers, which allow for simple image viewing, to more advanced systems that offer tools for measuring, annotating, and analyzing images. DICOM viewers can be standalone applications or integrated into PACS and other imaging systems.
-
Mobile and Web-Based Viewers: With the rise of mobile and web technologies, DICOM images can now be accessed on smartphones, tablets, and web browsers. These viewers are designed to be lightweight and user-friendly while maintaining the integrity and quality of the DICOM images. DICOMweb, a web-based extension of the DICOM standard, facilitates this type of access.
-
-
3D Reconstruction and Advanced Visualization Systems
As medical imaging technology advances, the need for more sophisticated tools to analyze and visualize images has grown. DICOM-compatible systems now include 3D reconstruction software and advanced visualization platforms. These tools allow radiologists and other healthcare professionals to create detailed 3D models from DICOM images, enhancing the ability to diagnose and plan treatments.
Features of DICOM-Compatible Systems
-
Interoperability
One of the key features of DICOM-compatible systems is interoperability. This means that devices and systems from different manufacturers can work together seamlessly, allowing for the smooth exchange of images and data. This is critical in healthcare settings where patient data needs to be accessible across different departments and locations.
-
Scalability
DICOM-compatible systems are designed to be scalable, meaning they can grow with the needs of a healthcare organization. Whether a small clinic or a large hospital, DICOM systems can be expanded to handle increased volumes of images and data, ensuring that the system remains efficient and effective as the organization grows.
-
Data Security
Ensuring the security of patient data is a top priority in healthcare, and DICOM-compatible systems are built with robust security features. These systems support encryption, secure transmission protocols, and access controls to protect sensitive patient information from unauthorized access and breaches.
-
Comprehensive Image Management
DICOM-compatible systems offer comprehensive image management capabilities, including image storage, retrieval, and sharing. These systems can handle large volumes of images, organize them by patient or study, and ensure that they are easily accessible when needed. This is particularly important in large healthcare organizations where managing image data can be complex.
-
Integration with Healthcare IT Systems
DICOM-compatible systems are designed to integrate with other healthcare IT systems, such as EHRs and HIS (Hospital Information Systems). This integration allows for the seamless flow of information between different systems, providing healthcare professionals with a complete view of the patient’s medical history and current condition.
-
Advanced Image Processing
Many DICOM-compatible systems include advanced image processing tools that allow healthcare professionals to enhance and manipulate images for better diagnosis and treatment planning. These tools can include functions like image filtering, contrast adjustment, and the ability to view images in different planes and dimensions.
How to View and Analyze DICOM Data
-
Using DICOM Viewers
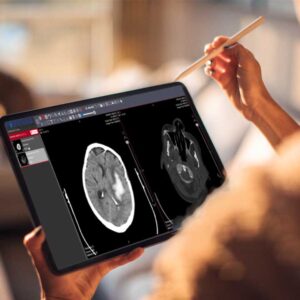
DICOM viewers are the most common tools for viewing and analyzing DICOM data. These viewers can be standalone applications or part of a larger PACS or RIS system. DICOM viewers typically offer a range of tools for interacting with images, including zoom, pan, rotate, and the ability to adjust image contrast and brightness. Some viewers also offer more advanced features, such as 3D reconstruction and image fusion, which are essential for certain types of medical imaging.
-
With the advent of DICOMweb, accessing DICOM data via the web has become increasingly common. Web-based DICOM viewers allow healthcare professionals to view and analyze images from any device with an internet connection. This is particularly useful for remote consultations, second opinions, and telemedicine. Web-based access also facilitates the integration of DICOM data with other web-based healthcare applications, such as electronic health records and patient portals.
-
Mobile DICOM Access
Mobile devices have become an essential tool in healthcare, and many DICOM-compatible systems now offer mobile access to DICOM data. Mobile DICOM viewers allow healthcare professionals to view and analyze images on the go, whether they are in the hospital, at a remote location, or even at home. These viewers are typically designed to be user-friendly and optimized for smaller screens, making them an effective tool for quick image review and analysis.
-
Integration with AI and Machine Learning
As artificial intelligence and machine learning continue to advance, DICOM-compatible systems are increasingly integrating these technologies to enhance image analysis. AI algorithms can be trained to recognize patterns and anomalies in DICOM images, assisting radiologists and other healthcare professionals in making more accurate diagnoses. This integration is still in its early stages but has the potential to revolutionize the way medical images are interpreted.
Conclusion
DICOM-compatible systems are the backbone of modern medical imaging, providing the tools and infrastructure needed to store, share, and analyze medical images. From imaging modalities like MRI and CT scanners to advanced visualization systems and mobile viewers, these systems ensure that medical images are accessible, secure, and interoperable across different platforms and devices.
Understanding the features and capabilities of DICOM-compatible systems is essential for anyone involved in healthcare, as these systems play a critical role in patient care and medical decision-making. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovations in DICOM-compatible systems, further enhancing their capabilities and expanding their role in healthcare.
In future blog posts, we will explore how DICOM files contain detailed patient information and the implications this has for patient care, data security, and interoperability. Stay tuned for more insights into the world of medical imaging and healthcare technology.