Do not opt out of the medical image archive to reduce costs!
Digital medical imaging accounts for approximately %70 of all clinical data stored worldwide.
Medical images are the biggest capital of hospitals and form a large part of the patient’s medical record.
Medical image archiving policies vary around the world, and many countries have not updated their policies since the beginning of digital imaging.
This delay in updating has been accompanied by a misperception of the medical image archive.
What is the duration of the medical images archive?
Policy-making organizations or even some medical centers have set special standards regarding record keeping policies.
Each country’s storage archives differs from country to country, but it requires healthcare organizations to make imaging studies available for an average period of 10 years, but most countries have special regulations for children. Due to the importance of medical images, healthcare organizations do not delete medical image.
With the growth of digital pathology imaging, this amount is sure to increase.
Managing this data puts a huge burden on health IT organizations.
Reduce IT efforts
Increasing storage arvhives requirements and complexity conflict with the time and staffing constraints of IT departments. Clinics and hospitals can deal with this challenge with automation and outsourcing.
Studying and reviewing images, understanding the clinical and forensic requirements for preserving medical images and how to use new data storage technologies can have a significant impact on imaging data management.
Optimizing the method of storing and retrieving information
Storage equipment must have many capabilities including fast access to information, credibility, security and stability of informationProper selection of storage equipment will reduce costs.
Secure data storage for archived medical images
Secure data storage for archived medical records is a regulatory imperative. Make sure your organization has the right solution.
Information life cycle management
When most imaging professionals hear the term information lifecycle management, they think of policy-based deletion.
In fact, removing medical images is just the wrong way to go according to the policy of some healthcare organizations.
Another aspect of information management is the use of lossless data compression techniques to reduce the volume of medical images, also allowing images to be used for high-quality interpretation and diagnosis by radiologists.
Information life cycle management is an efficient tool for maintaining and archiving medical images, which is cheaper by transferring older imaging to the storage level, and is used to manage medical image archives with easy retrieval for study and research.
Storage archives requirements and considerations
- Data retention and information life cycle management
- Reliability of accuracy and authenticity of archival information
- Ability to cover requirements
- Ensuring security and complying with the data security standard in the HIPPA health system
- Prevent unauthorized changes to information
- Appropriate compression of information due to their high volume
- Recover data and records at any time
- Archives of medical images along with medical reports included in the patient file, and storage of data related to medical images
The key difference between data archiving and data backup
Data backup and data archiving are two terms that are often mentioned in the same role, and on the surface it may seem almost the same. However, both involve making a copy of the data for future use.
Backup and archive are actually used for completely different purposes
Archives are for space management, compliance, risk aversion and long-term preservation.
Backup is for recovery from hardware failure or recent data corruption or loss.
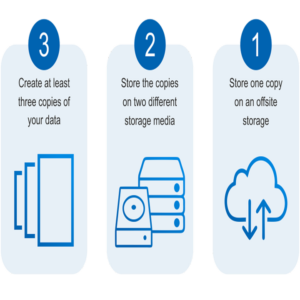
Safe strategy, 3-2-1 model
One of the reliable ways to archive sensitive storage of organizations is to keep two or three copies of information.
But information security does not only mean keeping multiple copies of information, but also requires a reliable and appropriate strategy for information protection.
This issue is one of the most basic and sensitive issues for organizations and senior managers of information technology, which consumes the time and energy of many specialists.
The US-CERT organization has introduced an architectural model called the “3-2-1” model, which reduces the risk of data loss and is recommended for backup.
3 means: keeping three copies of important files, each copy in the storage layer
2 means: storing files on two different media
1 means: keeping a copy of the files offline (out of the site)