In medical terms, PACS stands for Picture Archiving and Communication System.
As healthcare organizations become more digital and more specialties are generating data and images, the need to store and share all of this data electronically increases.
PACS is a medical imaging technology that allows archiving, storing, communicating, and transferring of digital images produced by different imaging methods in hospitals and medical centers.
Instead of using the old method of manual photography, recovery, and transport of film negatives, this system stores images and reports electronically.
PACS is the right solution to solve the problems of physical archiving, retrieval, and sending of film jackets.
An electronic PACS provides economical storage, rapid retrieval of images, access to images obtained by multiple methods, and simultaneous access at multiple sites.
Medical imaging storage technologies such as PACS are increasingly important as the volume of digital medical images increases throughout the healthcare industry and data analysis of those images becomes more common.
PACS architecture:
The architecture of the physical implementation of the required functionality is different from what one sees from the outside. Depending on the user, there are different views. A radiologist typically sees an observation station, a technician a QA workstation, while a PACS administrator may spend most of his time in a climate-controlled computer room.
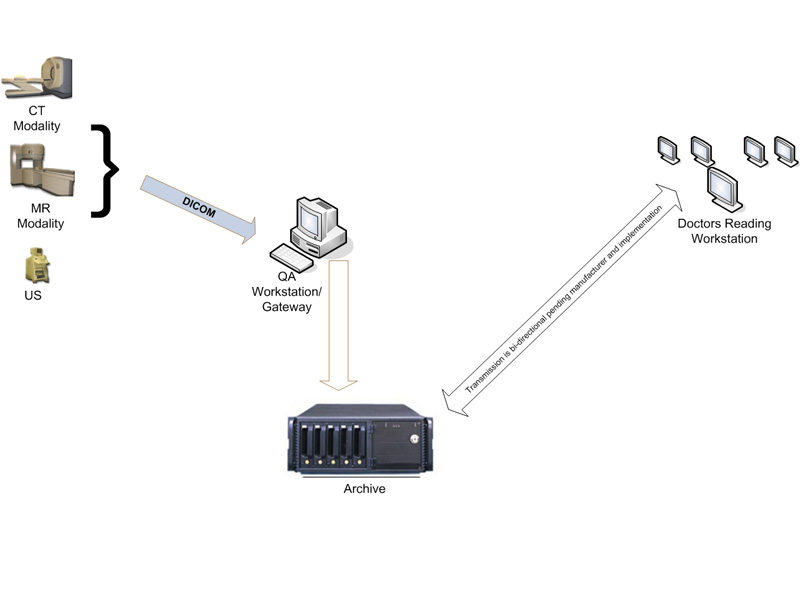
Typically, a PACS consists of a multitude of devices. The first step in conventional PACS systems is modality. Modalities are usually computed tomography (CT), ultrasound, nuclear medicine, positron emission tomography (PET), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Depending on the facility’s workflow, most modalities are sent to a quality assurance (QA) workstation, sometimes called a PACS gateway.
The QA workstation is a checkpoint to ensure patient demographics, as well as other important characteristics of a study, are correct. If the study information is correct, the images are sent to the archive for storage. The central storage device (archive) stores images and in some cases reports, measurements, and other information contained in the images. The next step in the PACS workflow is reading workstations. The reading workstation is where the radiologist reviews the patient’s reading and formulates a diagnosis.
Backup images in PACS
PACS image backup is an important, but sometimes overlooked, part of the PACS architecture. HIPAA requires that a backup copy of patient images be made in the event of image loss from PACS. There are several ways to back up images, but they usually involve automatically sending copies of the images to a separate computer for storage, preferably off-site.
Who uses PACS?
This system is used to store, retrieve, present, and share images produced by various medical hardware methods, such as X-ray scanning, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound devices, endoscopy (ES), Mammography (MG), radiography (DR), computed radiography (CR), ophthalmology and even clinical departments beyond radiology such as cardiology, oncology, orthopedics, and nuclear medicine and even laboratories that are creating medical images are stored in the PACS system. are created and managed.
In addition to storing and viewing images with the original DICOM quality, radiologists and specialists can use different specialized and efficient measurement tools, view the image from different angles, and diagnose and provide their clinical reports on the medical images of patients.
Therefore, all people and specialist doctors and radiologists who deal with digital medical images and imaging Modalities need PACS.
Click here to learn more about DICOM
What protocol does PACS use to communicate with imaging Modalities?
PACS follows the DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) protocol for secure storage and transmission of patient images.
DICOM is the most basic global standard for storing and transferring medical images.
DICOM allows PACS systems to communicate and exchange data with imaging devices including the DICOM standard.
The Components of PACS
There are four main components of PACS:
- An Imaging modality for performing patient scans to produce a medical image
- Creating a secure and high-speed network for uploading and transferring images
- Creating suitable workstations for radiologists and specialist doctors simultaneously to review images
- Archiving and storage of medical images
Benefits of PACS
Alternative to hard copies: It is a great alternative to print-based medical images and film archives. Since the development of technology, the cost of data storage is decreasing, by using PACS software, you can save physical space for data storage and reduce costs in addition to immediate access to images and data.
Remote access: By giving access to people outside the center for viewing and reporting that includes remote diagnostics. This allows doctors in different locations to access the same information for remote diagnosis.
Creating a platform for electronic image integration: providing an electronic platform for connecting images with several other medical systems such as Hospital Information System (HIS), Radiology Information System (RIS), Electronic Medical Record (EMR)
Radiology department workflow management: The PACS system is used by radiology personnel to manage patient treatment workflow.
In addition to the general advantages above, the use of the PACS system for diagnosis, doctors, patients, and hospitals also has advantages, which are briefly mentioned.
Advantages of diagnosis
- Better access to past and current patient records
- Integration with the patient file and increase the speed of retrieval
- Possibility of better diagnosis
- Improving the quality of patient care
Benefits of referral to a doctor
- Better management of patient treatment process
- Possibility of faster and better diagnosis
- Reducing the duration of visits and treatment
- Reducing legal costs due to mismanagement in losing images, not having a patient record, and things like that
Benefits for patients
- Reduction of X-ray radiation from radiology equipment due to less need to retake images
- Reduction of examination time
- Increasing patient satisfaction
Benefits for the hospital
- Help to communicate better with doctors
- Improving hospital management
- Better education for students with access to online video files and digital educational files
- Retention of employees due to reduced work pressure
Other benefits
- Ability to save standard 2D and 3D images
- Reduce the number of similar images
- Fast and efficient data management
- Displaying the patient’s radiology history in time view
- It allows the doctor to view the images even before the patients return to the examination room.
- Healthcare practitioners in remote areas can easily access radiology data.
- Even though radiologists are the primary users of PACS, the software is now incorporated into several other medical fields such as pathology, cardiology, oncology, dermatology, nuclear medicine imaging, etc.
Enter your information to learn more about MINNOVAA.